Belt and Road Initiative: Key Success Stories of China’s Global Partnerships
Introduction
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) is a global development strategy launched by China in 2013. It aims to strengthen economic connectivity, infrastructure, and trade across Asia, Europe, and Africa through investment and cooperation. The initiative has garnered international attention for its scale and scope, involving over 140 countries and international organizations. Through the Belt and Road Initiative, China has fostered significant global partnerships, leading to successful projects that have boosted trade, created jobs, and improved regional connectivity. This article explores key success stories of China’s global partnerships under the Belt and Road Initiative, highlighting how these collaborations have contributed to economic growth and mutual prosperity.

What is the Belt and Road Initiative?
The Belt and Road Initiative encompasses two main components: the Silk Road Economic Belt, which focuses on overland routes across Central Asia and Europe, and the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road, which aims to strengthen sea routes through Southeast Asia, the Indian Ocean, and beyond. The Belt and Road Initiative has evolved into a vast network of infrastructure projects, including roads, railways, ports, and energy pipelines. Its goal is to create a new era of trade routes that facilitate seamless movement of goods and services between continents. By understanding the vision behind the Belt and Road Initiative, one can appreciate its potential to reshape global trade patterns and promote economic integration, Read this complete article click here.

Why Global Partnerships Matter in the BRI
Global partnerships are the backbone of the Belt and Road Initiative, enabling China to collaborate with countries across different regions to achieve shared development goals. These partnerships allow China and its partner countries to pool resources and expertise, leading to faster project implementation and economic benefits. Through the Belt and Road Initiative, China has developed a reputation for delivering large-scale infrastructure projects that address critical needs such as energy shortages and transportation bottlenecks. These partnerships not only strengthen diplomatic ties but also foster trade and investment flows, creating a win-win situation for China and its partners. The emphasis on mutual cooperation has been key to the success of the Belt and Road Initiative.
Key Success Stories of China’s Global Partnerships
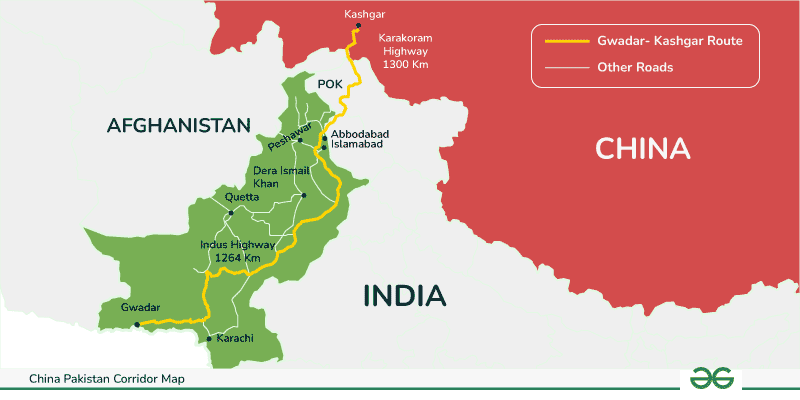
- China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC):
The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) is one of the most notable success stories of the Belt and Road Initiative. This multi-billion-dollar investment connects Gwadar Port in Pakistan to China’s Xinjiang region through a network of highways, railways, and pipelines. CPEC has led to the development of Gwadar Port into a strategic trade hub, enhancing Pakistan’s maritime trade capabilities. Additionally, CPEC has helped Pakistan address chronic energy shortages through power projects, contributing to industrial growth and job creation. The Belt and Road Initiative has thus enabled Pakistan to strengthen its infrastructure and economy, while China gains a vital link to the Arabian Sea. - Mombasa-Nairobi Standard Gauge Railway, Kenya:
In East Africa, the Mombasa-Nairobi Standard Gauge Railway (SGR) stands as a testament to successful collaboration under the Belt and Road Initiative. This modern railway has dramatically reduced travel time between Mombasa and Nairobi, facilitating the efficient movement of goods and people. As part of the Belt and Road Initiative, this project has boosted Kenya’s economy by increasing trade efficiency, attracting foreign investment, and creating thousands of jobs. The SGR also plays a crucial role in regional integration by providing a blueprint for connecting other East African nations, demonstrating the broader impact of the Belt and Road Initiative in Africa. - Port of Piraeus, Greece:
The Port of Piraeus has become a vital gateway for trade between Asia and Europe, thanks to investment under the Belt and Road Initiative. COSCO, a state-owned Chinese shipping company, acquired a majority stake in the port, transforming it into one of the busiest container ports in Europe. The Belt and Road Initiative has revitalized the Port of Piraeus, increasing container throughput and streamlining logistics. This development has benefited both Greece’s economy, through job creation and increased trade, and China’s access to European markets. The Belt and Road Initiative has thus positioned the port as a key node in the global supply chain. - China-Europe Freight Train Service:
The Belt and Road Initiative has also successfully expanded overland trade between China and Europe through the China-Europe Freight Train Service. This rail network offers a faster and more cost-effective alternative to sea routes, connecting Chinese cities like Chongqing, Chengdu, and Xi’an with major European hubs such as Duisburg in Germany and Madrid in Spain. The service has significantly boosted trade, reducing transport time from 45 days by sea to around 15-18 days by rail. By enhancing trade links, the Belt and Road Initiative has not only supported the growth of Chinese exports but has also strengthened economic ties between China and European countries. - China-Laos Railway:
The China-Laos Railway is another landmark project under the Belt and Road Initiative. This railway connects Kunming in China’s Yunnan province with Vientiane, the capital of Laos, spanning over 1,000 kilometers. As part of the Belt and Road Initiative, the railway has improved transportation efficiency between the two countries and is expected to drive economic growth in Laos by opening up new trade and tourism opportunities. For China, the project strengthens its links to Southeast Asia, enhancing regional connectivity and fostering economic development. This success story highlights the Belt and Road Initiative’s role in bridging development gaps and promoting regional integration.
Common Themes Among Successful BRI Projects
The BRI has transformed infrastructure development in many regions, with common themes emerging across successful projects. Key elements include large-scale investment in transportation networks, modernization of ports, and creation of energy infrastructure. These projects have enhanced trade routes, making it easier for countries to access global markets. Furthermore, the Belt and Road Initiative has been instrumental in creating employment opportunities and stimulating local economies. By focusing on projects that address critical infrastructure needs, the Belt and Road Initiative has managed to drive economic growth and development, fostering stronger ties between China and partner nations.
Challenges and Criticisms of the Belt and Road Initiative
Despite its successes, the BRI has faced challenges, including concerns about debt sustainability and the environmental impact of large-scale projects. Critics argue that some countries have taken on significant debt to fund BRI projects, raising concerns about their long-term economic stability. Additionally, environmental and social challenges have emerged in areas where infrastructure projects have disrupted ecosystems and local communities. Addressing these criticisms is crucial for the BRI to maintain its momentum and ensure that future projects are sustainable and inclusive.
Future of the Belt and Road Initiative and Global Partnerships
The Belt and Road Initiative continues to expand, with new regions and projects on the horizon. China is exploring opportunities to extend the initiative into Latin America, the Arctic, and even digital infrastructure through the Digital Silk Road. As the BRI evolves, it remains focused on building mutually beneficial partnerships. By fostering collaboration in fields like technology, green energy, and digital trade, the BRI aims to adapt to global challenges while continuing to drive economic integration and development. Watch similar article from wikipedia.
Conclusion
The Belt and Road Initiative has proven to be a transformative force in global development, with numerous success stories of China’s collaboration with other countries. From enhancing infrastructure in Africa to creating new trade routes with Europe, the BRI has fostered economic growth and strengthened global connectivity. As the initiative continues to evolve, its emphasis on partnerships will remain a cornerstone of its success. The BRI stands as a symbol of the power of cooperation and shared progress in the 21st century.